A Verb in Grammar is one of the most important parts of speech. It is the word that tells us what the subject does, what happens, or what state something or someone is in. In simple terms, a verb shows action, state, or occurrence.
Let’s break that down
- Action Verbs — These verbs show what a person, animal, or thing is doing.
- Examples: run, play, eat, sing, write
- Rohan runs every morning.
- They write in their notebooks.
- The dog barked loudly.
- Examples: run, play, eat, sing, write
- State Verbs — These verbs show a condition or state of being, not an action.
- Examples: is, am, are, seem, feel
- She is happy today.
- It seems cloudy.
- I feel tired after school.
- Examples: is, am, are, seem, feel
so, when we talk about a Verb in Grammar, we are talking about the word that makes the sentence come alive. Without verbs, we would just have a list of nouns that don’t make sense together.
For example:
Riya homework school. (No meaning!)
Riya does her homework after school. (Meaningful because of the verb does)
That’s the power of verbs — they connect the subject to the action or idea.
Difference Between Verbs and Other Parts of Speech

| Part of Speech | Role in Sentence | Example |
| Noun | Names a person, place, or thing | dog, school, Riya |
| Adjective | Describes a noun | happy, tall, red |
| Verb | Shows action or state | run, is, play |
| Adverb | Describes how an action happens | quickly, slowly |
As you can see, the Verb in Grammar is the engine of every sentence — it moves everything forward and gives meaning to the subject.
Importance of Verbs in Grammar

A Verb in Grammar is like the engine of a car — without it, nothing can move! Every complete sentence needs a verb to make sense. Verbs tell us what the subject is doing or what condition it’s in. That’s why verbs are often called the heart of English sentences.
Imagine trying to speak without using a verb. You wouldn’t be able to say what’s happening! For example:
The boy football. (Incomplete)
The boy plays football. (Complete — because of the verb plays)
This simple example shows how important verbs are for expressing actions, feelings, and ideas clearly.
1. Verbs Give Life to Sentences
Without verbs, words just sit there. But when you add a Verb in Grammar, the sentence starts to move. For example:
- Birds fly in the sky.
- The sun shines brightly.
- Children laugh and play.
Here, fly, shines, and play are verbs that show life and movement.
2. Verbs Show Time (Tense)
Verbs also tell us when something happens — in the past, present, or future.
- I walk to school every day. (Present)
- I walked to school yesterday. (Past)
- I will walk to school tomorrow. (Future)
Knowing how to change a Verb in Grammar helps you speak and write correctly about time and action.
3. Verbs Build Strong Communication Skills
Understanding verbs makes your sentences clearer and more meaningful. Studies show that children who understand verb tenses early develop stronger reading and writing skills.
When you master verbs, you can describe events, tell stories, and express emotions easily.
In short, a Verb in Grammar is not just another word — it’s what makes your sentences work. Learning to use verbs correctly helps you become confident in English speaking, reading, and writing.
Types of Verbs in Grammar
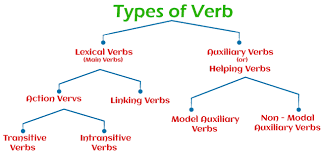
A Verb in Grammar can be of many types, each serving a special role in a sentence. Understanding these types helps us know how actions, states, and ideas are expressed in English. Let’s look at each type with simple definitions and examples!
1. Action Verbs
These verbs show what someone or something does. They can be physical or mental actions.
- Physical Action: run, jump, eat, swim
- Mental Action: think, dream, believe, remember
Examples: - She runs every morning.
- I think about my future.
2. Linking Verbs
These verbs don’t show action. Instead, they link the subject with information about it. Common linking verbs include is, am, are, was, were, seem, and feel.
Examples:
- He is a doctor.
- The soup tastes delicious.
Here, the verb connects the subject (He, The soup) to what describes it.
3. Helping Verbs (Auxiliary Verbs)
A Verb in Grammar sometimes needs a helper to form tenses, questions, or negatives. Helping verbs include is, am, are, have, has, do, does, will, can, and may.
Examples:
- She is reading a book.
- They have finished their work.
4. Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
- Transitive verbs have an object.
- She kicked the ball.
- She kicked the ball.
- Intransitive verbs don’t need an object.
- She laughed loudly.
- She laughed loudly.
5. Regular and Irregular Verbs
- Regular verbs form past tense by adding -ed (walk → walked, jump → jumped).
- Irregular verbs change completely (go → went, eat → ate, write → wrote).
Each Verb in Grammar plays a unique part in making sentences meaningful. Whether it’s running, being, helping, or linking, verbs bring sentences to life.
Functions of Verbs in Grammar

A Verb in Grammar is more than just an action word — it’s what makes a sentence complete and meaningful. Every sentence needs a verb because verbs show what the subject does, is, or feels. Let’s explore the main functions of verbs in simple terms.
1. Verbs as the Heart of a Sentence
In English, every complete sentence has a verb. Without it, a sentence cannot express a complete thought.
Examples:
- Riya sings beautifully. (The verb sings tells what Riya does.)
- The sun shines brightly. (The verb shines shows the action of the sun.)
Here, the verb acts as the predicate, telling us what the subject is doing.
2. Verbs Show Time (Tense)
One of the most important functions of a Verb in Grammar is to show when something happens — past, present, or future.
Examples:
- I play football every day. (Present)
- I played football yesterday. (Past)
- I will play football tomorrow. (Future)
By changing the verb form, we can express time and make sentences clearer.
3. Verbs Express Conditions or Feelings
Some verbs express states, emotions, or conditions rather than actions. These include is, am, are, was, feel, seem, and appear.
Examples:
- She feels happy today.
- He is a teacher.
These verbs help describe who or what someone or something is.
4. Verbs Help Form Questions and Negatives
Helping verbs like do, does, did, can, have, and will are used to form questions or negatives.
Examples:
- Do you like apples?
- She does not play cricket.
In short, a Verb in Grammar holds the sentence together — it shows the action, tells the time, expresses feelings, and helps us form questions. Without verbs, language would lose its rhythm and meaning!
Common Mistakes with Verbs in Grammar

Even though verbs seem simple, many students make small mistakes when using them. A Verb in Grammar changes its form depending on who is doing the action and when it happens. Learning these rules helps you avoid confusion and write correct sentences every time.
Let’s look at some of the most common verb mistakes — and how to fix them!
1. Confusing Countable vs. Uncountable Contexts
Sometimes, students use the wrong verb form when the subject changes.
Examples:
- Wrong: He go to school every day.
- Correct: He goes to school every day.
Remember: When the subject is he, she, or it, add -s or -es to the verb in the present tense.
2. Using the Wrong Tenses show when an action happens — past, present, or future. Mixing them up can confuse the meaning.
Examples:
- Wrong: I eat breakfast yesterday.
- Correct: I ate breakfast yesterday.
The past tense of eat is ate.
3. Misusing Helping Verbs
Helping verbs like do, does, did, have, and will support the main verb.
Examples:
- Wrong: She not like mangoes.
- Correct: She does not like mangoes.
Always use a helping verb before “not” in negative sentences.
4. Forgetting Subject–Verb Agreement
The Verb in Grammar must match the subject in number (singular or plural).
Examples:
- Wrong: They was playing.
- Correct: They were playing.
Use was for singular and were for plural subjects.
5. Mixing Regular and Irregular Verbs
Regular verbs add -ed in the past tense, but irregular verbs change completely.
Examples:
- Wrong: He goed home.
- Correct: He went home.
Quick Tip:
Read your sentence aloud! If it doesn’t sound right, the verb might need changing.
A Verb in Grammar follows patterns — once you learn them, you’ll never get stuck again. Keep practicing,
Tips to Identify a Verb in Grammar

Finding a Verb in Grammar is like finding the heartbeat of a sentence — it’s the word that shows what’s happening! Once you learn a few simple tricks, spotting verbs becomes super easy.
Here are some fun and helpful ways to identify verbs quickly
1. Look for the Action Word
The easiest way to find a Verb in Grammar is to look for the word that tells what someone or something is doing.
Examples:
- Riya dances beautifully. → (dances is the verb)
- The birds fly high. → (fly is the verb)
If it shows an action, it’s probably a verb!
2. Check if the Word Shows a State or Condition
Not all verbs show action. Some tell us about a state of being or feeling.
Examples:
- He is tired. (is shows a state)
- I feel happy. (feel shows emotion)
So, verbs can describe both what we do and how we are.
3. Find the Word That Changes with Time (Tense)
A Verb in Grammar changes form depending on when the action happens — past, present, or future.
Examples:
- play → played → will play
- go → went → will go
If a word changes with time, it’s definitely a verb!
4. Use “to” as a Clue (Infinitive Form)
Sometimes, verbs appear with “to” before them — like to run, to dance, to read.
Examples:
- I like to read books.
- She loves to sing.
5. Ask the Right Question
Try asking “What is happening?” or “What does the subject do?”
Example:
In The cat sleeps on the sofa, ask “What does the cat do?” → sleeps is the verb!
In short, a Verb in Grammar is the action or state word that gives life to a sentence. Once you know how to spot verbs, understanding grammar becomes simple and fun!
Examples of Verbs in Grammar
Now that we’ve learned what a Verb in Grammar is and how to identify it, let’s look at some real examples! Verbs are used in every sentence we speak, write, or read. They tell us what’s happening and make our words come alive.
Simple Examples in Sentences
Let’s see how verbs work in different types of sentences:
- Riya runs fast. → (The verb runs shows action.)
- He is happy today. → (The verb is shows a state.)
- They are playing football. → (The verb are playing shows an action happening now.)
- The sun rises in the east. → (The verb rises shows a natural action.)
- I will read my book later. → (The verb will read shows a future action.)
- She felt tired after school. → (The verb felt shows emotion.)
- We have finished our homework. → (The verb have finished shows completion.)
In each of these sentences, the verb makes the sentence meaningful. Without it, we wouldn’t know what is happening!
Table of Verb Types and Examples
| Type of Verb in Grammar | Definition | Examples |
| Action Verb | Shows what someone or something does | run, jump, eat, write |
| Linking Verb | Connects the subject to information about it | is, am, are, seem, feel |
| Helping Verb | Supports the main verb to show tense or mood | have, is, will, can |
| Transitive Verb | Needs an object to complete meaning | She reads a book. |
| Intransitive Verb | Doesn’t need an object | He sleeps. |
| Regular Verb | Adds -ed in past tense | walk → walked |
| Irregular Verb | Changes completely in past tense | go → went, eat → ate |
Quick Fact!
Did you know that “be” (is, am, are, was, were) is the most common Verb in Grammar in English? It appears more than 10% of the time in everyday speech and writing!
In short, verbs are the doers of English — they show what’s happening, when it’s happening, and how. Once you learn how to spot and use them, your sentences will become clear, powerful, and full of action!
Practice Section: Test Your Knowledge of Verbs in Grammar
Now that you’ve learned what a Verb in Grammar is, it’s time to test your understanding! Practicing verbs is the best way to remember how they work. These short exercises will help you spot verbs easily and use them correctly in your own writing.
Part 1: Identify the Verbs
Read each sentence carefully and underline or write the verbs you find.
- The dog barks loudly.
- She is reading a storybook.
- We played cricket yesterday.
- The flowers smell sweet.
- I will go to the park.
Tip: Remember — the Verb in Grammar tells you what’s happening or what state something is in!
Part 2: Fill in the Blanks with the Correct Verb
- Riya _______ (dance / dances) beautifully.
- The sun _______ (rise / rises) in the east.
- They _______ (is / are) playing football.
- I _______ (was / were) tired last night.
- He _______ (write / writes) a letter every day.
Hint: Always match the verb with the subject — “He writes,” not “He write.”
Part 3: Choose the Correct Verb Type
| Sentence | Type of Verb |
| She is a good dancer. | Linking Verb |
| The baby laughed loudly. | Action Verb |
| They are watching TV. | Helping + Action Verb |
| He went home early. | Irregular Verb |
Fun Fact!
The word “do” is one of the most powerful verbs in English. It can be used to form questions (Do you play cricket?), negatives (I don’t know), and even emphasize actions (I do like ice cream! ).
Quick Challenge:
Write three of your own sentences using verbs that show past, present, and future actions.
Example:
- Past: I played football yesterday.
- Present: I play football every day.
- Future: I will play football tomorrow.
Practicing verbs every day helps you become more confident in English. So, keep exploring how a Verb in Grammar works — because every sentence needs one!
Understanding Verbs in Grammar
Now that you’ve learned everything about Verb in Grammar, you can proudly say that you understand one of the most important parts of English! Verbs are the heart of every sentence — without them, we wouldn’t know what’s happening, who is doing what, or when the action takes place.
Recap of What We Learned
Let’s quickly go over the main points:
- A Verb in Grammar tells us about an action, state, or event.
Example: She runs fast. (runs = action) - Verbs can be action verbs (run, play, jump), linking verbs (is, am, are), or helping verbs (have, will, can).
- They also change form based on tense — past, present, or future.
Example: play → played → will play - Verbs make our speech and writing clear, strong, and meaningful.
Why Verbs Matter
Every time you speak or write, you use verbs — even if you don’t realize it! For example:
- I am eating breakfast.
- The birds fly in the sky.
- He will visit tomorrow.
Each of these sentences has a verb that shows what’s happening. That’s why understanding Verb in Grammar helps students build better sentences, improve writing, and communicate confidently.
According to English learning studies, students who understand verbs early on are 40% better at forming correct sentences as they progress in school. So, verbs aren’t just grammar — they’re your tool for fluency!
Final Thought
Mastering Verb in Grammar is like learning how to make your words move! Once you know how verbs work, you can express anything — what you did, what you’re doing, or what you will do.
Keep practicing verbs in fun ways — through songs, stories, or games — and you’ll soon become a grammar pro!
Next up: Read our upcoming post — “Adjectives in Grammar: Definition, Types, and Examples.”





