An Adjective in Grammar is a word that describes a noun or a pronoun. It tells us more about a person, place, thing, or idea — like what kind, how many, or which one. Adjectives make our sentences more colorful and meaningful by adding details.
For example, instead of saying “The car moved,” you can say “The red car moved fast.” The words red and fast are adjectives because they describe the car. Without adjectives, sentences sound plain and boring.
Definition of an Adjective in Grammar
A Adjective in Grammar is used to describe or modify a noun. It helps us understand qualities such as size, color, shape, feeling, or number.
Examples:
- A tall building (describes size)
- A sweet mango (describes taste)
- Three kittens (shows number)
In short, adjectives give meaning and life to words.
Types of Adjectives
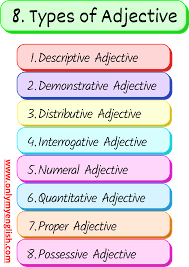
Here are the main types of adjectives you’ll often see in English:
- Descriptive Adjectives – Show qualities (beautiful flower, cold water).
- Quantitative Adjectives – Show quantity (some sugar, few apples).
- Demonstrative Adjectives – Point out things (this book, those shoes).
- Possessive Adjectives – Show ownership (my bag, their car).
- Interrogative Adjectives – Used in questions (which color, whose pen).
- Numeral Adjectives – Show number or order (first prize, two books).
Each type helps make your sentences more specific and clear.
Why Adjectives Matter

Using adjectives helps you write better stories and express ideas clearly. For example:
- A bright rainbow appeared after the rain.
- The small puppy slept peacefully.
When you understand how an Adjective in Grammar works, you can describe anything better — from people and places to your favorite foods!
So next time you speak or write, try adding a few adjectives — they’ll make your words shine!
What Is an Adjective in Grammar?

An Adjective in Grammar is a word that tells us more about a noun (a person, place, thing, or idea). It adds meaning by describing the noun’s quality, color, size, shape, or quantity. In simple words, adjectives make sentences more interesting and meaningful.
Think of adjectives as words that add color to your language. For example, when you say “a tall building,” “a red apple,” or “five pencils,” the words tall, red, and five are adjectives because they tell us more about the nouns — building, apple, and pencils.
Without adjectives, sentences would sound plain. Imagine saying “I saw a dog.” Now add adjectives — “I saw a cute, brown dog.” Doesn’t that sound better? That’s how adjectives make communication more descriptive and fun!
What Adjectives Tell Us
An Adjective in Grammar helps describe:
- Quality: beautiful flower, honest boy
- Color: red balloon, green leaf
- Size: big elephant, small bag
- Shape: round table, square box
- Quantity: two apples, many books
These little words add details that help readers or listeners imagine what you’re describing.
Adjectives vs. Other Parts of Speech

It’s easy to confuse adjectives with other words, but here’s how they differ:
- Nouns name things (car, school, dog).
- Verbs show action (run, eat, play).
- Adjectives describe nouns (fast car, big school, playful dog).
For example:
- In “The boy runs fast,” fast describes how he runs — it’s an adjective.
- In “The boy runs,” runs is the verb — it shows the action.
So, an Adjective in Grammar is a describing word that makes your writing brighter and your speech clearer. Whether it’s a colorful butterfly, a tasty pizza, or a happy child, adjectives help us express our thoughts beautifully!
Importance of Adjectives in Grammar
Adjectives are like magic words that make our sentences come alive! An Adjective in Grammar adds beauty, detail, and emotion to the way we speak and write. Without adjectives, language would sound flat and boring — like a drawing without colors.
For example, if you say “I have a dog,” it doesn’t tell us much. But if you say “I have a cute, playful dog,” now we can imagine it clearly! That’s what adjectives do — they help us see, feel, and understand things better.
How Adjectives Make Sentences Descriptive

An Adjective in Grammar tells us how something looks, feels, tastes, or sounds. It helps paint a picture in the reader’s mind. Look at these examples:
- Plain sentence: The flower bloomed.
- With adjectives: The beautiful red flower bloomed in the garden.
See the difference? The second sentence is more interesting because adjectives describe the flower’s color and beauty.
Adjectives also help us express emotions and opinions. For example:
- A happy child (emotion)
- A delicious cake (taste)
- A noisy classroom (sound)
These words make reading and listening more fun and engaging!
Why Learning Adjectives Is Important

Understanding Adjective in Grammar helps students speak and write better English. When you know how to use adjectives correctly, you can describe things clearly and make your thoughts easier to understand.
For instance:
- The sky is blue.
- The tall tree gives shade.
- The shiny stars twinkle at night.
Each sentence becomes vivid and meaningful because of the adjectives.
So, adjectives don’t just decorate words — they give life to your language. They make writing colorful, conversations expressive, and stories more enjoyable!
Types of Adjectives in Grammar
There are many kinds of adjectives in English, and each type tells us something special about a noun. Let’s explore the main types of Adjectives in Grammar with easy definitions and examples!
1. Descriptive Adjectives
These adjectives describe the quality or nature of a noun.
- Example: a beautiful flower, a tall boy, a cold drink
Here, beautiful, tall, and cold tell us more about the nouns.
2. Quantitative Adjectives
They tell us how much or how many of something there is.
- Example: some water, few apples, many books
These words talk about the quantity of nouns.
3. Demonstrative Adjectives
They point out which person or thing is being talked about.
- Example: this pen, that car, these oranges, those chairs
This, that, these, and those are commonly used demonstrative adjectives.
4. Possessive Adjectives
They show ownership or belonging.
- Example: my bag, your shoes, their house
Here, the words my, your, and their tell us who owns the noun.
5. Interrogative Adjectives
Used when asking questions about nouns.
- Example: Which book do you like? Whose car is this? What color is your bag?
They always come before a noun and help in asking questions.
6. Numeral Adjectives
These show numbers or order.
- Example: one apple, five pens, second chance
7. Proper Adjectives
Formed from proper nouns and always begin with a capital letter.
- Example: Indian food, American flag, French perfume
An Adjective in Grammar helps us express details clearly — whether we talk about quality, number, or ownership. By learning these types, you’ll understand how to describe people, places, and things more beautifully!
Position of Adjectives in Grammar
In English, adjectives don’t just describe — they also have a special place in a sentence. Knowing where to put an adjective helps us form sentences that sound natural and correct. Let’s learn where an Adjective in Grammar usually appears!
1. Before a Noun (Attributive Position)
Most of the time, an Adjective in Grammar comes before the noun it describes. This is called the attributive position.
Examples:
- A big balloon
- A red apple
- An honest boy
- The old tree
Here, the adjectives (big, red, honest, old) come before the nouns (balloon, apple, boy, tree). They give more information about the noun directly.
2. After a Verb (Predicative Position)
Sometimes, adjectives come after a verb — especially after linking verbs like is, am, are, was, and were. This is known as the predicative position.
Examples:
- The sky is blue.
- The cake tastes sweet.
- The children are happy.
- The flowers smell fresh.
In these sentences, the adjectives (blue, sweet, happy, fresh) describe the noun but appear after the verb.
Quick Tip
A simple way to remember this rule:
- If you are naming something → put the adjective before the noun.
- If you are describing a state or feeling → put the adjective after the verb.
So, the Adjective in Grammar can appear before or after the noun, depending on what you want to say. Understanding this position helps you write smoother, more natural sentences — and makes your English sound amazing!
Degrees of Adjectives in Grammar
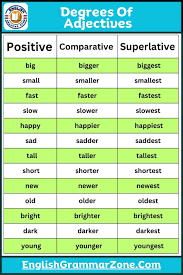
An Adjective in Grammar doesn’t just describe — it can also compare! Sometimes we use adjectives to show how people, places, or things are different in degree or quality. These are called the degrees of adjectives.
There are three main degrees:
- Positive Degree
- Comparative Degree
- Superlative Degree
Let’s understand them one by one with simple examples!
1. Positive Degree
The positive degree simply describes a noun without comparing it to anything else.
Examples:
- Riya is tall.
- The flower is beautiful.
- This pizza is tasty.
Here, we are only describing, not comparing.
2. Comparative Degree
The comparative degree is used when we compare two people, places, or things.
We usually add –er to short adjectives or use more before longer adjectives.
Examples:
- Riya is taller than Meena.
- This book is more interesting than that one.
- Today is colder than yesterday.
The adjectives taller, more interesting, and colder show a comparison between two nouns.
3. Superlative Degree
The superlative degree shows that something has the highest or lowest quality among three or more nouns.
We usually add –est to short adjectives or use most before longer ones.
Examples:
- Riya is the tallest girl in the class.
- This is the most beautiful painting.
- Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world.
The words tallest, most beautiful, and highest show the greatest degree of comparison.
Quick Tip
An Adjective in Grammar helps you express comparison clearly — from describing one thing to comparing several. So next time you describe something, ask yourself: Am I just describing, comparing two, or comparing many? That will tell you which degree to use!
Functions of Adjectives in Grammar
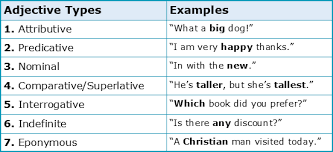
An Adjective in Grammar plays an important role in every sentence. It doesn’t just decorate nouns — it gives them meaning, clarity, and detail. Adjectives tell us what kind, how many, and which one, helping us understand nouns more clearly. Let’s look at how adjectives work in sentences.
1. Adjective as a Modifier of a Noun
The most common job of an Adjective in Grammar is to modify or describe a noun. It gives extra information about the noun’s quality, color, size, or quantity.
Examples:
- A beautiful garden (describes quality)
- A red car (describes color)
- A small kitten (describes size)
- Five apples (describes number)
Without these adjectives, the sentences would sound dull and incomplete.
2. Adjective as a Subject Complement
Sometimes, an adjective comes after a linking verb (like is, are, was, were) to describe the subject of the sentence.
Examples:
- The weather is pleasant.
- The soup tastes delicious.
- The children are excited.
Here, the adjectives (pleasant, delicious, excited) give more information about the subject.
3. Adjective as an Object Complement
An adjective can also describe the object of a sentence — the thing receiving the action.
Examples:
- The movie made her happy.
- The joke made everyone laughing.
- The teacher found the test easy.
These adjectives describe how the object felt or appeared.
Why It Matters
When used correctly, an Adjective in Grammar makes your speech and writing more colorful and meaningful. It helps readers and listeners imagine exactly what you’re describing — whether it’s a shiny car, a sweet mango, or a noisy classroom!
Common Mistakes with Adjectives in Grammar

Even though adjectives are easy to use, students often make small mistakes while describing nouns. Learning about these errors helps you use adjectives correctly and confidently. Let’s look at some common mistakes with Adjectives in Grammar — and how to fix them!
1. Using Adjectives Instead of Adverbs
Many learners confuse adjectives with adverbs. Remember — an Adjective in Grammar describes a noun, while an adverb describes a verb.
Wrong: She runs quick.
Right: She runs quickly.
Here, runs is an action (verb), so we need an adverb (quickly), not an adjective (quick).\
2. Wrong Word Order
When using more than one adjective before a noun, we must place them in the correct order — usually:
Opinion → Size → Age → Color → Origin → Material → Noun
Wrong: A cotton white nice shirt.
Right: A nice white cotton shirt.
Getting the order right makes your sentence sound natural!
3. Mixing Up Comparative and Superlative Forms
Students sometimes confuse comparative (–er, more) and superlative (–est, most) forms.
Wrong: This house is more bigger than that one.
Right: This house is bigger than that one.
Wrong: She is the most smartest student.
Right: She is the smartest student.
Only one comparative or superlative word is needed — not both!
4. Using Double Negatives
Wrong: This test is not difficult no more.
Right: This test is not difficult anymore.
Always use a single negative word to make your meaning clear.
Quick Tip
An Adjective in Grammar should always match the noun it describes — in meaning, number, and sense. The more you practice, the more naturally adjectives will fit into your sentences!
Tips to Identify Adjectives in Grammar
Finding adjectives in a sentence is easy once you know what to look for! An Adjective in Grammar is a word that describes a noun or pronoun — it tells us what kind, how many, which one, or how much. Here are some simple tips to help you spot adjectives quickly.
1. Look for Describing Words
The easiest way to find an Adjective in Grammar is to ask the question:
What kind of?
Which one?
How many?
Examples:
- The blue sky (What kind of sky?)
- Three kittens played (How many kittens?)
- That old book is mine (Which book?)
Words like blue, three, and old describe the nouns sky, kittens, and book.
2. Check the Word Before a Noun
In most cases, an adjective comes before a noun.
Examples:
- A beautiful dress
- An honest man
- A round table
If a word appears right before a noun and describes it — it’s likely an adjective!
3. Find Words After a Linking Verb
Sometimes, adjectives appear after verbs like is, are, was, were, seems, or feels.
Examples:
- The tea is hot.
- The baby looks cute.
- The flowers smell fresh.
Here, hot, cute, and fresh are adjectives describing the nouns tea, baby, and flowers.
4. Try Removing the Word
If removing the word makes the sentence less descriptive, it’s probably an adjective!
The tall boy ran fast.
Remove “tall” → The boy ran fast.
The sentence still works, but it loses detail — that’s how you know “tall” is an adjective.
Quick Practice Tip
When reading or writing, underline all the words that describe people, places, or things. Most of them will be Adjectives in Grammar!
Examples of Adjectives in Grammar
Examples are the best way to understand how adjectives work in sentences. An Adjective in Grammar can describe how something looks, feels, tastes, sounds, or behaves. Let’s look at a few examples to see how they bring sentences to life!
Simple Sentence Examples
The red balloon flew away.
She wore a beautiful dress.
The hungry puppy ate the food.
We saw three stars in the sky.
The cake smells delicious.
In each of these sentences, the adjective (in bold) tells more about the noun — balloon, dress, puppy, stars, and cake.
Without these adjectives, the sentences would still make sense, but they would be dull and colorless!
Table of Adjective Types and Examples
| Type of Adjective in Grammar | Example Sentence | Adjective | Describes |
| Descriptive | The happy child laughed. | happy | child |
| Quantitative | She has two pencils. | two | pencils |
| Demonstrative | That car is fast. | that | car |
| Possessive | My book is on the table. | my | book |
| Interrogative | Which movie did you watch? | which | movie |
| Numeral | He stood first in class. | first | position |
| Proper | I love Indian food. | Indian | food |
Why Examples Matter
Seeing real examples helps you remember how to use adjectives naturally. An Adjective in Grammar makes your sentences clear, interesting, and fun to read — whether you’re describing a bright morning, a tasty snack, or a kind teacher.
Practice Exercise on Adjectives in Grammar
It’s time to test what you’ve learned! Adjectives make sentences colorful and descriptive — now let’s see if you can spot and use them correctly.
Each activity below will help you identify and understand the Adjective in Grammar in different situations. Ready? Let’s go!
Exercise 1: Identify the Adjective
Read each sentence carefully and underline the adjective.
Example: The blue car is parked outside.
- The tall tree touched the sky.
- My brother has a new bicycle.
- The soup tastes delicious.
- I have three pencils in my box.
- The little puppy is sleeping.
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks
Choose the correct adjective from the brackets to complete each sentence.
- The weather is _______ today. (sunny / sings)
- She wore a _______ dress for the party. (beautiful / quickly)
- The elephant is a _______ animal. (big / slowly)
- My teacher is very _______. (kind / kindness)
- This pizza looks _______. (tasty / taste)
Exercise 3: Compare Using Degrees of Adjective
Write the correct form of the adjective in brackets.
- This book is _______ than that one. (interesting)
- Mount Everest is the _______ mountain in the world. (high)
- Riya is _______ than Meena. (tall)
- The test was _______ than yesterday’s. (easy)
- This apple is _______ of all. (sweet)
Exercise 4: Think and Describe!
Pick one noun — like your school, your pet, or your favorite food.
Now, write five adjectives to describe it!
Example:
My cat: cute, soft, playful, white, lazy
Quick Tip
Practicing with examples helps you remember how to use adjectives easily. The more you read and write sentences with Adjectives in Grammar, the more natural your English will sound!
Conclusion on Adjectives in Grammar
Adjectives are truly the artists of language! They make our sentences colorful, expressive, and full of life. An Adjective in Grammar helps us describe people, places, animals, and things in a way that makes them easier to picture and understand.
Whether it’s a tasty cake, a happy child, or a beautiful sunset, adjectives bring meaning and imagination to every line we write or speak. Without them, our sentences would sound plain and dull — like a story without feelings or colors!
Learning about Adjective in Grammar also helps improve your writing and speaking skills. You can express your thoughts more clearly, describe experiences better, and even make your school essays more interesting to read.
Key Takeaways
- Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns.
- They tell us what kind, how many, which one, or how much.
- They can appear before a noun or after a linking verb.
- Adjectives can show comparison using degrees — positive, comparative, and superlative.
What’s Next?
Now that you know everything about Adjective in Grammar, you’re ready to move on to the next topic — Adverbs in Grammar: Definition, Types, and Examples!
Keep learning with Nap and Learn — where grammar becomes simple, colorful, and fun!